Shows dust

IMG: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ex0603_img/33panolamaS.jpg
Caption: People entering the city for rescue and relief
Approx. 1,180m from the hypocenter, Yamaguchi-cho (now, Kanayama-cho)
This panoramic shot extends from the burnt plain of the city to the west side of Hiroshima Higashi Police Station. People are heading toward the city center along the burnt-out streetcar street to join rescue efforts or search for loved ones
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/exhibit_e/exh0603_e/exh060307.html
Shows the power of the blast forces – compare with bent and hurled tridents

Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ex0603_img/52kusunoki.jpg
The large camphor trees of Kokutaiji Temple
Approx. 420m from the hypocenter, Ko-machi (now, Naka-machi) 52
In the graveyard of that temple grew four camphor trees said to be 300 years old. The trunk of the largest was seven meters in diameter. These trees were considered living natural treasures. When the streetcar line was built, the track was diverted away from the trees and the sidewalk was raised to avoid harming their roots. These beloved trees were toppled by the blast and consumed by the fire. All four died.
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/exhibit_e/exh0603_e/exh060309.html

The heat and blast are so severe that they can kill, and destroy buildings, for up to five miles from the explosion. Beyond that, there can be severe damage.
http://www.cercidas.com/Nukes/ProtectAndSurvive/protect_and_survive.htm (dead URL)

For the man-in-the-open example above, that’s 2.2 miles from the detonation of a 500 KT air burst where the shock wave would arrive about 8 seconds after the detonation flash, this sharp body slap would produce a 10-psi overpressure over his body that might perforate his eardrums. Additionally, though, he would experience a blast of wind of about 295 mph for about three seconds that would launch him careening into a probably fatal impact and he would also likely suffer injuries from flying missile fragments of glass and debris.
http://www.radshelters4u.com/#100

Glaser PDF
Impact of fizzle-yield explosion
(Area of complete destruction)

Source: Ted Postol, MIT

Caption: The blast cloud from a 50-megaton bomb, shown at right, reaches into the stratosphere
Img: http://howto.wired.com/mediawiki/images/thumb/Nukecloud.png/800px-Nukecloud.png
URL: http://howto.wired.com/wiki/Survive_a_Nuclear_Blast
Blast Effect on Structures
This photo sequence shows a wood-frame house exposed to a nuclear blast at the Nevada Test Site. The test was Upshot-Knothole Annie, a 16 Kt tower shot, on March 17, 1953. The house is 1,100 meters from ground zero.

The exposure to thermal radiation was 25 cal/cm2, about one-quarter of that experienced at ground zero in Hiroshima.
The blast overpressure was 5 psi, and the blast wave created surface winds of 160 mph (257 kpm).
http://www.atomicarchive.com/Photos/Blast/index.shtml
Atomic Archive videos
Blast wave hitting vehicles – movie
VIDEO: “BLASTWAVE1” Blast wave in nuclear explosion (Dailymotion)
“A fraction of a second after a nuclear explosion, a high-pressure wave develops and moves outward from the fireball. The blast effect of a nuclear explosion is produced by the heating of air by the fireball. Footage from several nuclear tests demonstrate the effects of the blast wave’s tremendous force on various vehicles” (Atomic Archive)
Larger video at Atomic Archive

Vehicles in atomic tests – movie
VIDEO: “Vehicles” from AtomicArchive (Dailymotion)

Blast wave video 2
VIDEO: “Blastwave2” from AtomicArchive (Dailymotion)
“A fraction of a second after a nuclear explosion, a high-pressure wave develops and moves outward from the fireball. The blast effect of a nuclear explosion is produced by the heating of air by the fireball. Footage from several nuclear tests demonstrate the effects of the blast wave’s tremendous force on vehicles and various structures.” (AtomicArchive)
Larger version from AtomicArchive

Blast wave video 3
VIDEO: “BLASTWAVE3” (Dailymotion)
Larger version of video at AtomicArchive
A fraction of a second after a nuclear explosion, a high-pressure wave develops and moves outward from the fireball. The blast effect of a nuclear explosion is produced by the heating of air by the fireball. Footage from several nuclear tests demonstrate the effects of the blast wave’s tremendous force on vehicles and various structures. (AtomicArchive)

Blast wave video 4
VIDEO: “BLASTWAVE4” Blast wave from nuclear explosion. (Dailymotion)
Larger version can be watched at AtomicArchive

Blast Effects on Structures
“This shows a wood-frame house exposed to a nuclear blast at the Nevada Test Site. The test was Upshot-Knothole Annie, a 16 Kt tower shot, on March 17, 1953. The house is 1,100 meters from ground zero.
The exposure to thermal radiation was 25 cal/cm2, about one-quarter of that experienced at ground zero in Hiroshima.
The blast overpressure was 5 psi, and the blast wave created surface winds of 160 mph (257 kpm).” (AtomicArchive)

Still from the video
Overpressure from the Twin Towers explosions
“Rather, seismologists report, the buildings around the Twin towers were impacted both by the kinetic energy of the falling debris and by the pressure exerted on them by a dust- and particle-laden blast produced by the collapse.” (ScienceDaily)
Excerpts from the History Channel 9/11 video
Look how this steel is bent! Jet fuel softens steel?
VIDEO: “Look how this steel is bent! Jet fuel softens steel?”(Dailymotion)
Transcript: “We’ll have a crew of approximately 10 iron-workers to assist in offloading. We have a large forklift which will take a capacity of 50 tons.”
The only filing cabinet found
VIDEO: “The only filing cabinet found” (Dailymotion)
Transcript: ‘Perhaps the most astonishing object [Shea] found was something there should have been thousands of. This one only survived because it was in the basement. It belonged to an ice cream store. “I’d pretty much given up trying to find some sort of intact filing cabinet. But while I was at the compound for the Port Authority Police, this ball of metal about the size of a basketball was delivered to them. You can see what remains of the file folders that were inside.”’
“Haven’t seen a doorknob …”
VIDEO: “Haven’t seen a doorknob” (Dailymotion)
Transcript: “I haven’t seen a door, haven’t seen a phone, haven’t seen a computer, haven’t seen a doorknob.” (James Luongo, Deputy Inspector, NYPD)
Bent like a horseshoe
VIDEO: “Bent like a horseshoe” (Dailymotion)
Transcript: ‘This 8 ton steel I beam is six inches thick. It was selected to be preserved for future generations for the near-perfect horseshoe-like bend formed during the collapse.’
Recovery worker: “I found it hard to believe that it actually bent because of the size of it and how there’s no cracks in the iron. It bent without a single crack in it. It takes thousands of degrees to bend steel like this.”
Interviewer: “Typically you’d have buckling and tearing on the tension side but there’s no buckling at all.”
Video excerpts above are taken from video below:
History Channel: “Relics from the Rubble” (2002)
VIDEO: Full-length documentary from History Channel (51m27s)
ArchiveOrg | Youtube | Vidme Part 1 | Vidme Part 2
Average distance from hypocenter and kinds of damaged structures

Damage from Blast Pressure of the Standard A-bomb

http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2009a&l=e
Blast pressure and negative pressure

As the blast (shockwave) radiated outward, the air pressure at the epicenter (point of detonation) fell far below normal atmospheric pressure. This created a reverse blast wind blowing back toward the center.
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2009b&l=e
Damage from the A-bomb Blast
VIDEO: Negative pressure in A-bomb blast (Dailymotion | small version | larger version)
At the instant of detonation, the heat expanded the air suddenly, generating a blast carrying pressure of several hundred thousand atmospheres. At 500 meters from the hypocenter, the atmospheric pressure per square meter was a huge 19 tons (roughly fifteen automobiles), powerful enough to collapse almost every structure. People were killed when the blast threw them or collapsed the buildings they were in.
Image from video
Workings of A-bomb blast.
1. The atomic bomb exploded.
2. A super-hot fireball was generated, expanding the surrounding air with ferocious power.
3. A wall of air spread faster than sound.
4. The air behind this wall was a blast.
5. As the blast spread, the air pressure near the hypocenter plummeted from high to low in an instant (creating negative pressure).
6. The air blowing out from the hypocenter reversed direction; wind swept back in toward the center with tremendous force.
7. Negative pressure worsened the damage caused by the blast.
(URL)
Variations of overpressure and dynamic pressure with time

URL: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/1ch3.htm
Img: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/fig3-ii.gif
Variations of blast effects associated with positive and negative phase pressures with time

Img: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/fig3-iii.gif
URL: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/1ch3.htm

Img: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/fig3-i.gif
http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/1ch3.htm
Video showing negative pressure
VIDEO: Shows negative presure of nuclear blast (“EFFECTS2”) (Dailymotion | AtomicArchive)
FROM: AtomicArchive
Galvanized tin roofing

330m from the hypocenter
Fukuro-machi
This fell on the roof of Hiroshima Fukoku Building in Fukuro-machi.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/5101-0026.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2010a&l=e
Iron shutters bent by the blast

Donated by Property Affairs Division, General Affairs Department, Hiroshima Prefecture
2,670m from the hypocenter
Deshio-cho
The iron shutters of the Hiroshima Army Clothing Depot were bent by the blast. The roof of the building was badly damaged but escaped the fire. It became an emergency relief station immediately after the bombing. Many survivors received first-aid treatment there.
Width : 1,260mm
Height : 1,660mm
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/5101-0027.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2013&l=e
Wall with shards of glass

Donated by Morihisa Suzuki
2,500m from the hypocenter
Minami-danbara-cho(now Danbara-minami)
This is a part of the second floor wall of the western side of a house at the southeast foot of Hijiyama Hill. Despite being sheltered from the direct blast by the hill, glass fragments from shattered windows were carried by the deflected blast wind and pierced the wall.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/5105-0002.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2014&l=e
Part of a Column from Aioi Bridge Deformed by the Blast

300m from the hypocenter
This flange from a column supporting the Aioi Bridge was deformed by the powerful blast. The Aioi Bridge located in the heart of the city was the target of the atomic bombing. The concrete sidewalk 30 centimeters thick was lifted high by the blast reflecting off the river.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/5101-0029.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2015&l=e
Iron girders

Donated by Fukoku Mutual Life Insurance Company
330m from the hypocenter
Fukuro-machi
The iron frame in the ceiling of the top floor of the seven-story Hiroshima Fukoku building was bent and sheared by the pressure of the blast.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/5101-0028.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2017&l=e
Blast wind missiles

Img: http://www.911oz.com//image_db/image_repository/rec_57/x_image_1.jpg

Img: http://www.911oz.com//image_db/image_repository/rec_102/i_image_1.jpg
http://www.911oz.com/links/dummies/2?PHPSESSID=810f18a46d4764ec02dd551123fc76ee

The Three World Financial Center building is hit with North Tower shrapnel.
http://911speak.com/WTC/wtc.htm (dead link)

Closeup of the huge missile impaled into the building.
http://911speak.com/WTC/wtc.htm (dead link)


Img: http://doujibar.ganriki.net/english/e-wtc1_others/wintergarden-wallunit.jpg
http://doujibar.ganriki.net/english/e-03a-wintergarden.html

Note: the yellow line between WTC 1 and WFC 3 is 103 meters long.

World Financial Center is across the street from WTC 1 and is the building with the cross in the upper left.

You can see steel exterior beams that weigh many tons being ejected from the building by the force of the explosion. These beams then become missiles that fly outwards and land some distance away. This is not a straight-down pancake collapse.
Img: http://drjudywood.com/articles/why/whypics/54_explodingvolcano_017.jpg
http://drjudywood.com/articles/why/why_indeed.html

Supposedly the ‘puffs of air’ were strong enough to do this:
Closeup of the huge missile impaled into World Financial Center 3 across the street from the WTC.
Img: http://www.lescarney.com/Pictures/wtc_9_66.jpg
(Picture modified from the site below:
http://www.lescarney.com/wtc_9_11_untold_story.htm )
Red circled part is this:

Img: http://911research.wtc7.net/essays/reynolds/docs/cons_trusses.jpg
Picture modified from:
http://911research.wtc7.net/essays/reynolds/

Comment: They look like matchsticks but they’re heavy beams that weigh tons. See the picture below. Some of these beams were flung 400 meters.
Img: http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/analysis/collapses/docs/site1085_c.jpg
http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/analysis/collapses/steel.html

Img: http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/analysis/collapses/docs/site1085_c.jpg (enlarged section)
http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/analysis/collapses/steel.html

Img: http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/arch/docs/fig_2_7.jpg
http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/arch/perimeter.html
A close-up of the beams, some still held together, and some pieces weighing many tons.

Img: http://nuke.crono911.org/Portals/0/Foto4/24912199.jpg
URL: http://nuke.crono911.org/Crono911Aggiornamenti/FotoVideoMedia/WTC1e2Icollassi/tabid/76/Default.aspx

H-beams and I-beams fused into strange shapes with concrete.
Another URL: http://www.media-collections.com/pictures/index.html
A closeup of the beams above.
Explosive Ejections of Dust and Pieces
- Thick dust clouds spewed from towers in all directions, at around 50 feet/second.
- Solid objects were thrown ahead of the dust — a feature of explosive demolition.
- The steel was thoroughly cleansed of its spray-on insulation.
- Some pieces of the perimeter wall were thrown laterally 500 feet.
- Aluminum cladding was blown 500 feet in all directions.
- Blast waves broke hundreds of windows in buildings over 400 feet away.
http://911research.wtc7.net/talks/wtc/expulsion.html
Map showing where the columns and cladding of the Twin Towers ended up

IMG: http://www.debunking911.com/fig-1-7.jpg
http://www.indybay.org/newsitems/2006/04/09/18141561.php
WTC bars, girders and tridents



Trident


Some photos of steel at the JFK Hangar: http://blogs.wsj.com/photojournal/2010/11/22/911-artifacts-at-jfk-airport/

IMG: http://www.brickshelf.com/gallery/seankenney/Buildings/World-Trade-Center/04_comparison.jpg
http://www.seankenney.com/portfolio/world_trade_center/

IMG: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/newyork/sfeature/images/sf_gallery_07.jpg
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/newyork/sfeature/sf_gallery_07.html
Tridents come from the exterior of the Twin Towers. They formed the external arches at the base of the buildings.

An internal view of the tridents from the lobby of one of the Twin Towers.
Img: http://thefuntimesguide.com/images/blogs/world-trade-tower-1-lobby.jpg
http://thefuntimesguide.com/2006/09/september_11th.php
Force of blast made crosses out of beams

“The crosses are just shards of steel that came from the Tower 1 [the north tower], and went right through the roof of Building 6 and destroyed the entire center of it,” he explained.
Img: http://www.september11news.com/aaacrossoriginal.jpg
http://www.september11news.com/Mysteries1.htm

Img: http://www.september11news.com/AAACross1.jpg
http://www.september11news.com/Mysteries1.htm
http://911speak.com/WTC/wtc.htm

Another cross found in the rubble.
http://slatts.blogspot.com/2006_09_10_archive.html (moved)
Img: http://images39.fotki.com/v1292/photos/2/292835/2681563/wtc20cross-vi.jpg
URL: http://www.true2ourselves.com/forum/general-discussions/5176-9-11-prayer.html

Another view of the cross above.
Caption: The cross formed by girders that was left standing after the World Trade Center collapse.
Img: http://www.spurgeon.org/images/pyromaniac/wtccross.jpg
http://phillipjohnson.blogspot.com/2005_12_01_archive.html
Tridents

Img: http://www.brynmawr.edu/Acads/Cities/imgb/ax/3005/3005i.jpg
http://www.brynmawr.edu/Acads/Cities/imgb/ax/3005/3005m.html
The above is reduced to this:

Img: http://xcdn.me/by/7dz/images/2010/09/overview-of-the-wreckage-looking-west.jpg
http://photo-mond.t2i.info/architecture-history/world-trade-center-ground-zero-9-11/ (dead link)
Another URL: http://byrev.org/photovideo/911-photos-wtc-2001-ground-zero-photos/
Overpressure
Overpressure chart

Obviously, the bigger the weapon yield the larger the area of overpressure damage from the blast wave. But, notice that the damage range does not increase in a linear fashion with the more powerful explosions. For instance, comparing the 200 KT air burst with the five times more powerful 1 MT air burst, the range of moderate damage and initial fires increased from only 4.3 miles to 7.3 miles. This is because the reach of blast and fire effects varies as the cube root of the weapon yield ratio and the cube root of 5 is 1.71. So, instead of a five-fold increase or 500% we have only about a 70% increase in this comparison. [..]
All buildings will suffer light damage from the shock wave at even 1 psi peak overpressure–shattered windows, doors damaged or blown off hinges and interior partitions cracked. The maximum wind velocity would be only about 35 miles per hour. As the overpressure increases, so does the blast wind–exceeding hurricane velocities above about 2 psi.
So, how much blast or overpressure is too much to survive?
It, of course, depends on where you are when it comes charging through, but from a 500 KT blast, 2.2 miles away, it’ll be arriving about 8 seconds after the detonation flash. (An even larger 1 MT blast, but 5 miles away, would give you about 20 seconds.) Like surviving an imminent tornado, utilizing those essential seconds after the initial flash to ‘duck & cover’ could be the difference between life & death for many. Both the overpressure in the blast shock wave and the blast wind are important causes of casualties and damage.
http://www.radshelters4u.com/#100 (dead link)
Chronological development of an air burst

When the expanding blast wave from a nuclear air burst strikes the surface of the earth, however, it is reflected (Figure 3-I), and the reflected wave reinforces and intensifies the primary wave.
Img: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/fig3-I.gif
http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/1ch3.htm

Caption: Although American wood-frame houses offer less blast protection indoors than brick houses, they mostly have basements which are ideal for improvised shelters such as strong tables, because nuclear test data from OPERATION UPSHOT-KNOTHOLE at Nevada in 1953 and OPERATION TEAPOT at Nevada in 1955 showed that the blast winds carry most of the debris past the house, so that the debris load on the basement is minimal and survival is easy there (below).
http://glasstone.blogspot.com/2006/03/samuel-glasstone-and-philip-j-dolan.html
Failure of overpressure-sensitive structural elements

Img: http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/tab3-II.gif
http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/usa/doctrine/dod/fm8-9/1ch3.htm

Img: http://abolishnukes.com/charts/downloadable/nuclear_bomb_effects_part1_download.gif
URL: http://abolishnukes.com/charts/downloadable/
Blasted into dust

http://www.library.cornell.edu/olinuris/ref/911.html (moved link)

Img: http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Imgs/Jpg/MSH/Images/MSH80_volcanic_ash_collected_near_randle_1980s_med.jpg
URL: http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Volcanoes/MSH/Images/MSH80/framework.html
http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Volcanoes/MSH/Images/MSH80/may18_devastation.html

http://hakone.eri.u-tokyo.ac.jp/vrc/erup/14_15erup.html
BLAST and WIND
Damages Caused by the Blast (Nagasaki)
Ordinary wooden houses within a radius of one kilometer of the hypocenter were completely destroyed. Even the concrete buildings left standing were reduced to hollow shells. The buildings collapsed in one direction as if pointing toward the hypocenter. The blast wind slapped people against walls and showered them with a torrent of bullet-like glass splinters and debris.
Goes with this picture:

http://www1.city.nagasaki.nagasaki.jp/na-bomb/museum/m2-7e.html (moved)
Warehouse blast – movie
VIDEO: (Dailymotion)
The wind blew at 1,000 miles per hour—shattering the bodies of thousands of people as it hurled them through the air or brought buildings crashing down upon them.
When the firestorm died down, the former city was a scorched plain. A heavy black rain brought radioactive dust back down to earth. Some of the dead had been vaporized, many others lay where they died, in their thousands and thousands. [Hiroshima]
http://rwor.org/a/011/burning-hiroshima-nagasaki.htm
Mr. Sumiteru Taniguchi was a sixteen year old postal carrier at the time of the bomb. He was delivering mail on his normal route in Sumiyoshi town when the atomic bomb exploded. “After the sky flashed as lightning I was thrown with a bicycle on the ground when I came to around my skin on the left arm peeled off and hung down to fingertip, my back and hips were burned and became sore and clothes nearly didn’t remain. [Nagasaki]
http://users.dickinson.edu/~history/product/steele/seniorthesis.htm
The wind blew at 1,000 miles per hour—shattering the bodies of thousands of people as it hurled them through the air or brought buildings crashing down upon them.
When the firestorm died down, the former city was a scorched plain. A heavy black rain brought radioactive dust back down to earth. Some of the dead had been vaporized, many others lay where they died, in their thousands and thousands.
http://rwor.org/a/011/burning-hiroshima-nagasaki.htm
Patricia Ondrovic Interview
KT: When these vehicles blew up, was it kind of like what you would see in the movies where the vehicle pops up in the air when it explodes with a fireball coming out?
PO: I remember parts flying off — I think I got hit with a car door. I remember they were also on fire, but I don’t specifically recall the movie type fireball, but there was a loud bang as the door flew off the one car I was running past.
http://killtown.blogspot.com/2006/02/911-rescuer-saw-explosions-inside-wtc.html
Ondrovic Interiew – Buildings WTC 5 and 6 blowing up at the same time as WTC 2 (South Tower)
KT: Can you describe more about how the building blew up on you? Did you feel the shock wave from the explosion and/or debris falling down near you?
PO: Well, one second I was trying to put my stretcher into the ambulance, the next thing I know I am thrown to the ground as the ground was shaking. Debris was flying at me from where the building I was parked in front of. There was a continual loud rumbling, there was just debris flying from every direction and then everything being covered in the black and gray smoke.
KT: Let’s recap real quickly; your ambulance was parked backed up against the WTC 6, near the 6’s corner by the alleyway between the WTC 5 and 6 …
http://killtown.blogspot.com/2006/02/911-rescuer-saw-explosions-inside-wtc.html
“We start walking back there and then I heard a ground level explosion and I’m like holy shit, and then you heard that twisting metal wreckage again.” [James McKinley — E.M.T. (E.M.S.)]
http://www.whatreallyhappened.com/thermite.html (dead link)
Comment
“We start walking back there and then I heard a ground level explosion and I’m like holy shit, and then you heard that twisting metal wreckage again.” [James McKinley — E.M.T. (E.M.S.)]
http://www.whatreallyhappened.com/thermite.html (dead link)
Video – Force of the blast threw her onto the sidewalk
VIDEO: “911.wtc.glass.blew.out” (Dailymotion)
Transcript: “I was standing next to 1 World Trade Center and then all of a sudden I heard rumbling and we all started running away from it [talking about WTC 2 collapse]. The glass like blew out and threw me onto the sidewalk [Impact injury – minumum overpressure of at least 1.8 psi, probably experienced overpressure of 5] … and I couldn’t see for like twenty seconds…”
Wind
Keith Murphy — (F.D.N.Y.) [Engine 47] At the time, I would have said they sounded like bombs, but it was boom boom boom and then the lights all go out. I hear someone say oh, s___, that was just for the lights out. I would say about 3, 4 seconds, all of a sudden this tremendous roar. It sounded like being in a tunnel with the train coming at you. It sounded like nothing I had ever heard in my life, but it didn’t sound good. All of a sudden I could feel the floor started to shake and sway. We were being thrown like literally off our feet, side to side, getting banged around and then a tremendous wind starting to happen. It probably lasted maybe 15 seconds, 10 to 15 seconds. It seemed like a hurricane force wind. It would blow you off your feet and smoke and debris and more things started falling. Interview, 12/05/01, New York Times (pdf file)
http://911research.wtc7.net/wtc/evidence/oralhistories/shaking.html
GLASS
Glass embedded in wall (Hiroshima)

The concrete wall damaged by broken glass pieces
A part of a concrete wall from the Hiroshima Red Cross Hospital is preserved in a small park in front of the hospital. When the hospital was rebuilt, this part of the wall was removed from the old building and placed in the park. The wall was located opposite windows which faced North. Pieces of broken glass scratched the surface of the wall. Very small pieces of glass are sticking into the wall.
http://www.csi.ad.jp/ABOMB/RETAIN/wall.html (dead link)
Glass Fragment Expelled Naturally

Donated by Norio Nakabayashi
1,100m from the hypocenter
Hirose-kita-machi(now Hirose-cho)
Norio Nakabayashi (then, 17) was exposed to the bomb in the auditorium of Hirose Elementary School where he was stationed. He managed to escape from the collapsed building, but window fragments pierced his back and neck in about 120 places. He returned to his partially destroyed house in Eba on August 9, where he was confined to his bed for three months. This fragment emerged naturally from a swelling on his left cheek about 29 years after the bombing.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/7205-0002.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2002b&l=e
Surgically Removed Glass Fragment

Donated by Chiyoko Kosaka
1,000m from the hypocenter
Teppo-cho(now Kaminobori-machi)
Chiyoko Kosaka (then, 12), a first-year student at Hiroshima Jogakuin Girls High School, was exposed to the bomb in her house in Teppo-cho, 1,000 meters from the hypocenter. Glass fragments penetrated deep into her entire body, and she was trapped under the collapsed house. […] This glass fragment was surgically removed in August 1965, twenty years after the bombing.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ihin_img/7205-0001.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/cgi-bin/museum.cgi?no=2003&l=e
Hiroshima Atomic Bomb Museum, Artifacts
“The explosion created a supersonic shock wave which was responsible for destroying most of the buildings in the blast zone. Fully half of the bomb’s released energy was released in the form of this wind, which spread out at 440 meters per second (1600 km/hr or 1000 miles/hr; the speed of sound is 330 meters per second). It not only knocked things down, it also filled the air with debris. The section of concrete wall below has numerous glass shards embedded in it, even though it was 2200 meters (one and a half miles) from the hypocenter, and sheltered from the blast by a low hill.” [Hiroshima]
http://www.richard-seaman.com/Travel/Japan/Hiroshima/AtomicBombMuseum/IndividualArtifacts/
Yukiharu did not realize at first that a bomb had exploded. He thought there had been an electrical accident at the plant building he was working in. Then it suddenly became dark and “I heard a huge explosion. The roof of the building had collapsed, and we were under the broken roof. I felt a pain in my head. I managed to escape from the building. I did not know what was happening to us, because we had not experienced any serious bombing. . . . I was not badly hurt. . . . A piece of broken glass was sticking into my head.” [Hiroshima]
http://users.dickinson.edu/~history/product/steele/seniorthesis.htm
Ordinary wooden houses within a radius of one kilometer of the hypocenter were completely destroyed. Even the concrete buildings left standing were reduced to hollow shells. The buildings collapsed in one direction as if pointing toward the hypocenter. The blast wind slapped people against walls and showered them with a torrent of bullet-like glass splinters and debris.

http://www1.city.nagasaki.nagasaki.jp/na-bomb/museum/m2-7e.html (dead link)
Eiko Taoka, then 21, was one of nearly 100 passengers said to have been on board a streetcar that had left Hiroshima Station at a little after 8:00 a.m. and was in a Hatchobori area, 750 m from ground zero, when the bomb fell. Taoka was heading for Funairi with her one year old son to secure wagon in preparation for her move out of the building which was to be evacuated. At 8:15, as the streetcar approached Hatchobori Station, an intense flash and blast engulfed the car, instantly setting it on fire. Taoka’s son died of radiation sickness on August 28. The survival of only ten people on the streetcar have been confirmed to date.
When we were near in Hatchobori and since I had been holding my son in my arms, the young woman in front of me said, I will be getting off here. Please take this seat.’ We were just changing places when there was a strange smell and sound. It suddenly became dark and before I knew it, I had jumped outside…. I held [my son] firmly and looked down on him. He had been standing by the window and I think fragments of glass had pierced his head. His face was a mess because of the blood flowing from his head.Eiko Taoka, then 21, was one of nearly 100 passengers said to have been on board a streetcar that had left Hiroshima Station at a little after 8:00 a.m. and was in a Hatchobori area, 750 m from ground zero, when the bomb fell. Taoka was heading for Funairi with her one year old son to secure wagon in preparation for her move out of the building which was to be evacuated. At 8:15, as the streetcar approached Hatchobori Station, an intense flash and blast engulfed the car, instantly setting it on fire. Taoka’s son died of radiation sickness on August 28. The survival of only ten people on the streetcar have been confirmed to date.
http://www.atomicarchive.com/History/twocities/hiroshima/page14.shtml

Caption: A downtown Las Vegas window, showing how the glass was sucked out by the rarefaction wave, rather than pushed in by the compression wave resulting from the November 1, 1953, nuclear test at the Nevada Test Site.
[A] large window shattered outward in Fremont Street, Las Vegas, Nevada; Sears’ large show-windows fell out on the sidewalk, due to the 21 kt Dog test at the Nevada test site. This was due to the suction phase of the blast which had been focussed on Las Vegas by jet stream winds. The man responsible for predicting this damage, Jack Reed, blamed the test manager for firing the nuclear bomb under adverse conditions because the food had run out for 3,000 press and civil defense observers (see quotation from Reed’s site, above). A big window is more likely to fail than a small one. 0.03 psi is small compared to normal pressure (14.7 psi), but the force exerted on a big window is appreciable, for example a window 6 feet high and 10 feet wide subject to 0.03 psi gets 6 x 10 x 144 x 0.03 = 259.2 pounds of force (1153 Newtons). At great distances, the window often survives the inward push in the compression phase but then shatters when the low-pressure (rarefaction) phase occurs, pulling the window the other way suddenly. There is no significant flying glass hazard (except from vertically falling glass right beside the window), because the blast winds are too weak to accelerate fragments into high velocity missiles. Near the explosion there is a greater risk of this, but clothing or ‘duck and cover’ action offers good protection (see Glass Fragment Hazard from Windows Broken by Airblast, ADA105824 [..].)
http://glasstone.blogspot.com/
Video – Glass blew out and she was thrown onto sidewalk

“I was standing next to 1 World Trade Center and then all of a sudden I heard rumbling and we all started running away from it [talking about WTC 2 collapse]. The glass like blew out and threw me onto the sidewalk … and I couldn’t see for like twenty seconds…” (Video)


http://drjudywood.com/articles/dirt/dirt3.html

View from inside the World Financial Center
http://photo-mond.t2i.info/architecture-history/world-trade-center-ground-zero-9-11/ (dead link)

House in old Nevada test still standing with windows all blown out.
http://www.shundahai.org/area_1_nts.htm (dead link)
Glass shattered from vehicles’ windows






http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.htm
Blast effect on house 1 – movie
VIDEO: “House blast1″ (Dailymotion) FROM: AtomCentral
Blast effects on house 2 – movie
VIDEO: “House blast 2” (Dailymotion) FROM: AtomCentral
Forest blast – movie
VIDEO: “Forest” (Dailymotion)
FROM: AtomCentral
Palms blast – movie
VIDEO: “Palms” (Dailymotion) FROM: AtomCentral
Vehicles blasted

Notice the overturned vehicle in front of World Financial Center 2
http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html

No debris around to have caused these cars such damage.
http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/moretoastedcars.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/moretoastedcars.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/moretoastedcars.html

Where is the debris that twisted and crushed this car?
http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html

No large-sized debris where these cars are. Only fine powder dust.
http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html
Contrast picture with above

Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ex0603_img/46romendensya.jpg
Caption: The remains of a streetcar (model 100). Approx. 360m from the hypocenter, Togiya-cho (now, Kamiya-cho 1-chome). The model 100 was a wooden streetcar debuted on November 23, 1912, by Hiroshima Electric Railroad, predecessor to Hiroshima Electric Railway Company. Struck on the track as it headed out of town, it was completely burned.
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/exhibit_e/exh0603_e/exh060309.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html

What made the hood of this car crumple like that as if it were paper scrunched up?

Back then as now

Car turned into a pile of scrap
Approx. 320m from the hypocenter.
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ex0603_img/46romendensya.jpg
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/exhibit_e/exh0603_e/exh060309.html

Streetcar completely gutted by fire. Approx. 320m from the hypocenter
Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/ex0603_img/34densya.jpg
Caption: Approx. 320m from the hypocenter, Moto-machi. The streetcar packed with passengers was headed towards Hiroshima Station about 70 meters east of the Kamiya-cho intersection when the atomic bomb consumed it in fire. The stonewall visible behind the streetcar surrounded the Hiroshima Castle moat that then extended as far as the Aioi Bridge and Hatchobori.
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/exhibit_e/exh0603_e/exh060307.html
Charred streetcar

When the atomic bomb exploded, seventy streetcars were operating in Hiroshima. Near the hypocenter, several were burned black. Occupants died where they sat.
Caption: When the atomic bomb exploded, seventy streetcars were operating in Hiroshima. Near the hypocenter, several were burned black. Occupants died where they sat. Despite the devastation, streetcar service was restored between Koami-cho and Koi on August 9. In less than two months, most main lines were running again. With the center of the city still in ruins, the sight of moving streetcars greatly encouraged the survivors.
http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/visit_e/est_e/panel/A3/3202_1.htm
Hiroshima – near the hypocenter


Img: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/img/panel_img/3202_1.jpg
Remains of a streetcar (model 100)
Approx. 360m from the hypocenter, Togiya-cho (now, Kamiya-cho 1-chome)
The model 100 was a wooden streetcar debuted on November 23, 1912, by Hiroshima Electric Railroad, predecessor to Hiroshima Electric Railway Company. Struck on the track as it headed out of town, it was completely burned.
URL: http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/virtual/VirtualMuseum_e/exhibit_e/exh0603_e/exh060309.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/moretoastedcars.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/moretoastedcars.html

http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/moretoastedcars.html

Note the dust in the car park. These cars are likely to have been damaged in situ. See the reasoning below and the picture of the same carpark that shows the dust on the cars and in the car park. Dust must have settled this distance and settled after the cars had been toasted by the thermal energy of the nuclear blast of the WTC explosives. URL: http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html

Seems like only dust landed on these cars not heavy debris. This picture was taken before the dust was removed. It’s likely the cars were caught fire in situ in the car park. Note the blanket of dust on top of the cars. Compare it to the picture above, probably in the same parking lot, where the cars are not covered in dust and the yard has not been swept in some areas.
http://drjudywood.com/articles/DEW/StarWarsBeam5.html
Map of car park in above pictures

The map shows the location of the car park in relation to the WTC and the distance from it.

This aerial view, taken before the disaster, shows the distance from the WTC towers to the parking lot. The distance to the closest WTC tower can be calculated to be around 100 meters. Cars in this car park were set on fire and burned in situ – proof that thermal energy of the size consistent with a nuclear blast emanated from the explosions at the World Trade Center.
30-ton tridents twisted and bent like bendy wire
http://www.amny.com/entertainment/news/am-wtcrelics-pg2006,0,6613706.photogallery?index=15

http://www.amny.com/entertainment/news/am-wtcrelics-pg2006,0,6613706.photogallery?index=3

http://www.amny.com/entertainment/news/am-wtcrelics-pg2006,0,6613706.photogallery?index=15

Close-up of these 30-ton tridents

http://www.amny.com/entertainment/news/am-wtcrelics-pg2006,0,6613706.photogallery?index=15

Tridents bent, cut and shredded.
http://www.911research.com/wtc/evidence/photos/groundzero.htm (dead link)

Img: http://www.serendipity.li/wot/wtc_ch2b/fig-2-4.jpe
http://www.serendipity.li/wot/wtc_ch2.htm

Unknown URL.

Lobby of WTC 1
Img: http://photos1.blogger.com/blogger/5459/522/400/wtcinlobby1.jpg
http://covertoperations.blogspot.com/2006/11/wtc1-debris.html
What fired a 270-ton beam sideways?

http://www.cloakanddagger.de/_Grossmann/270%20tons/9-11_What_Fired_270_Tons_Sideways.htm (dead link)
Img: http://www.911research.com/wtc/evidence/photos/docs/gz_hd1391p36.jpg
URL: http://www.911research.com/wtc/evidence/photos/gzrescue2.htmlSee Scrapbook (9-11: What Fired 270 Tons Sideways?)
The twin towers in Manhattan collapsed on the morning of 9-11-1. When North Tower (WTC1) collapsed at 10:28 a.m., a steel beam weighing 600,000 pounds (270 metric tons) was fired sideways over the freeway and flew in the side of a neighboring building (the Amex building, WFC [World Financial Center] 3).
If the North Tower (WTC1) had merely collapsed, gravity would have pulled downwards but not sidewards. It takes an enormous energy to propel such a heavy steel beam such that it will fly for more than 390 feet through the air sideways, not downwards.
http://www.cloakanddagger.de/_Grossmann/270%20tons/9-11_What_Fired_270_Tons_Sideways.htm (dead link)
See Scrapbook (9-11: What Fired 270 Tons Sideways?)
Documentation from FEMA of this beam stuck in the WFC 3

The beam flew approximately 150 meters in horizontal distance and speared the World Financial Center.
http://www.photolibrary.fema.gov/photolibrary/photo_details.do?id=3942

The steel beam from the WTC 1 flew across the street and ended up impaling the WFC 3 (World Financial Center 3) 150 meters away in the supposed gravity collapse.
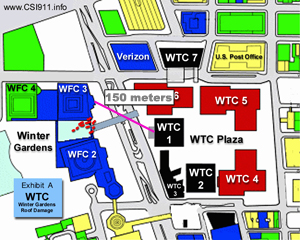
The steel beam flew a horizontal distance of 150 meters from the WTC1 to land in the World Financial Center with enough force to impale it. This does not happen in a gravity drop.
Chapter 7 of FEMA report: WFC3
The 50-story WFC 3 building has a plan area of approximately 200 feet by 250 feet. Exterior column trees from WTC 1 were found hanging from the southeast corner of WFC 3 (Figure 7-2) and on the setback roof and against the east face of the Winter Garden (Figures 7-3 and 7-4). The impact of exterior column trees caused structural damage in both structures. Building faces not directly oriented toward the WTC site suffered minimal damage, even at the close proximity of several hundred yards.The glazing and facade damage in the building was similar to that found in WFC 1 and WFC 2, which also had extensive cracking and breakage of glazing and granite panels. Debris from WTC 1 caused a collapse of the top 8 stories of the 10-story octagonal extension located at the southeast side of the building. The main WFC 3 building suffered damage from floors 17 to 26. A three-story section of exterior column trees from WTC 1 hung from the base of the collapsed area at floor 20, as shown in Figure 7-2, with approximately 25 feet of the column hanging outside the building. At floors 17 through 26, the corner column had been removed by the impact of debris, and the floors cantilevered from adjacent columns to the north and west. Smaller column debris penetrated floor 17. The damage did not extend past the corner bay, which had to be shored and was later demolished.
Interior damage is shown in Figure 7-5. Inspection of the interior determined that steel framing members that sustained direct impact from large debris had significant portions of the cementitious fireproofing material knocked off. The fireproofing was intact on adjacent steel members that had not been directly hit.
The localized nature of the damage, given the size of projectiles that impacted the building, is notable. Observations noted small welds between column end bearing plates at exterior and interior columns, indicating the columns near the damage zone were designed for gravity loads, and tension loads from wind were not a critical design parameter. This type of connection between columns may have allowed a column member to be knocked out of place without causing substantial displacement or damage to connecting framing.
http://911research.wtc7.net/mirrors/guardian2/wtc/WTC_ch7.htm
Pictures of WFC3 damage

Img: http://911research.wtc7.net/mirrors/guardian2/wtc/fig-7-2.jpg
Caption: Southeast corner of WFC 3.
http://911research.wtc7.net/mirrors/guardian2/wtc/WTC_ch7.htm

Figure 7-3 View of Winter Garden damage from West Street, with WTC 1 debris in front of WFC 2.
http://911research.wtc7.net/mirrors/guardian2/wtc/WTC_ch7.htm

http://911research.wtc7.net/mirrors/guardian2/wtc/WTC_ch7.htm
Figure 7-4 View of Winter Garden damage from West Street, with WTC 1 debris leaning against WFC 3.

http://www.cloakanddagger.de/_Grossmann/270%20tons/9-11_What_Fired_270_Tons_Sideways.htm
Summary of baseline ballistic data:
- spear-shaped projectile
- projectile weight 270 metric tons
- horizontal flight distance 160 meters
- loss of elevation during flight 325 meter
http://www.cloakanddagger.de/_Grossmann/270%20tons/9-11_What_Fired_270_Tons_Sideways.htm
________________________________________________________






